Definition: What is tooth root inflammation?
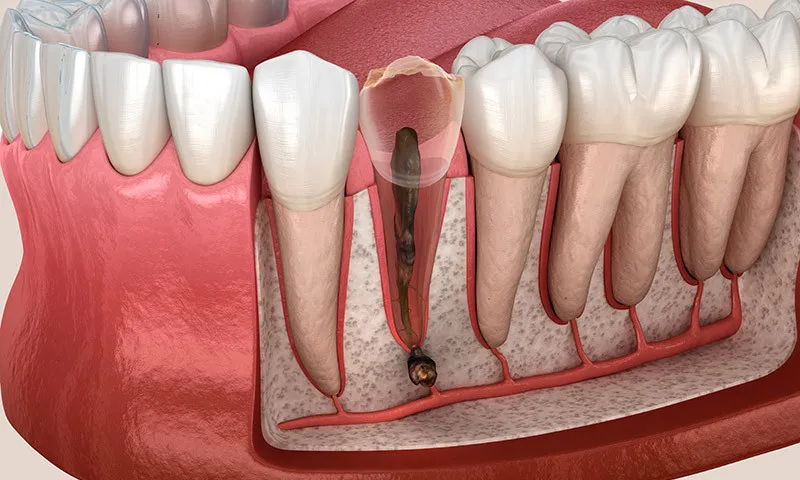
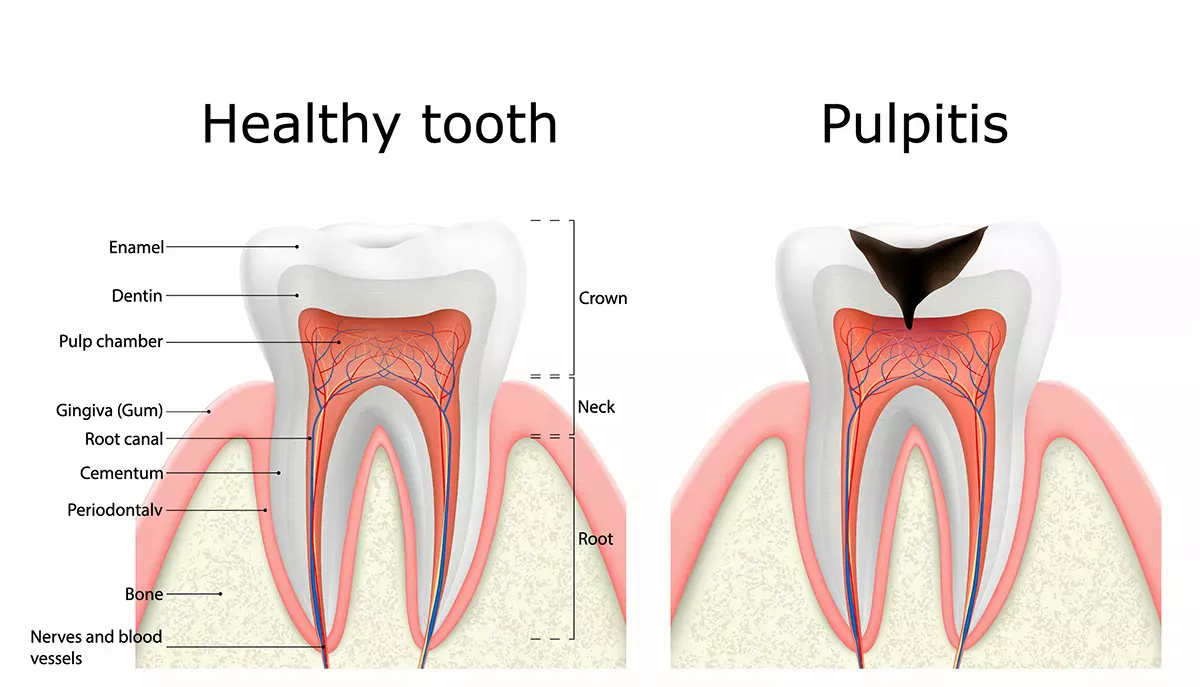
To understand what exactly root canal inflammation is, we first need to look at the structure of the tooth: The visible part of the tooth is the crown, below which is the neck of the tooth in the transition to the gums. The tooth is firmly anchored in the jawbone by the tooth roots. The tooth also consists of different layers: The outermost layer is the enamel - the hardest substance in the human body that protects the inside of the tooth. Beneath this is the dentin. The pulp, which consists of nerves and blood vessels, is hidden deep inside the tooth.
What is pulpitis?
Strictly speaking, the term "tooth root inflammation" is misleading because it could be assumed that it is exclusively an inflammation of the non-visible part of the tooth - i.e. the tooth root. In fact, medical experts refer to "pulp inflammation" (technical term pulpitis) and not inflammation of the tooth root. Pulpitis occurs when bacteria make their way into the inside of the tooth and trigger an inflammation in the pulp, which can then spread through the so-called root canals into the root of the tooth. The reason for the severe pain caused by inflammation inside the tooth is that the nerves are directly affected. If the inflammation is not treated, in the worst case scenario the nerve and therefore the tooth will die.
Colloquially, dental root inflammation is also referred to as root inflammation or dental nerve inflammation or simply as tooth inflammation.
Causes: How does tooth root inflammation develop?
The most common cause of tooth inflammation is tooth decay: If tooth decay is not treated early, the bacteria eat through the enamel and dentin into the tooth interior, where they attack the pulp. The body reacts with an inflammation to ward off the bacterial attack.
However, tooth root inflammation can also occur without caries. Periodontitis can also be the trigger for root inflammation: What begins as a harmless inflammation of the gums can develop into an inflammation of the periodontium. Gum pockets form in which bacteria can accumulate on the seam between the gum and tooth. At the same time, the gums recede, leaving the tooth necks exposed. As this part of the tooth is not protected by enamel, bacteria have an easy time and can spread to the root of the tooth.
Other causes of inflammation of the tooth root
Other reasons are less frequently responsible for tooth root inflammation. These include, for example
- Leaking fillings
- Crack in the tooth
- Broken tooth (for example after an accident)
- Teeth grinding
- Irritation due to wisdom teeth erupting at an angle
Good to know:
How exactly does tooth decay actually develop and what should you do if a tooth is affected? You can find all this and important tips on prophylaxis in our article:
Symptoms: What are the signs of tooth root inflammation?
Tooth root inflammation begins gradually: those affected initially suffer from teeth that are sensitive to pressure and pain, which are signalled by a sharp pain when biting into an apple or eating hot or cold food and drinks. In the early stages, patients can still name exactly where the pain starts.
Pain caused by inflammation of the tooth root
As soon as the inflammation has spread further, the main symptom appears: very severe, throbbing toothache. In the case of advanced root inflammation, the toothache can also spread to other areas of the jaw so that those affected can no longer say exactly where the pain is coming from. If tooth root inflammation is not treated, it will sooner or later reach the jawbone and cause the tissue around the tooth and bone to become inflamed. In this case, a very painful abscess can develop, which can also cause swelling - popularly known as a "fat cheek".
Good to know:
Here you can find out why you should never take an abscess lightly and how it is removed:
Symptoms of root inflammation of the gums
Root inflammation also leaves its mark on the gums: Initially, bleeding gums can easily occur when brushing your teeth because the gums are irritated. Bacterial infestation causes the gums to recede further and so-called gingival pockets form. Pus or secretions can be secreted here in the case of tooth root inflammation, which leads to an unpleasant bad breath.
No reason to be happy: abrupt cessation of pain
When the severe pain suddenly stops, sufferers are relieved at first. In reality, however, the abrupt cessation of pain is anything but good news: the nerve is so badly damaged that it no longer transmits pain signals to the brain. In other words, the tooth is dead. Nevertheless, treatment must be initiated immediately so that the tooth can be preserved. The dead tooth is still inflamed. If the inflammation is not removed, it will continue to spread. If the tooth can no longer be saved, it must be extracted. In fact, tooth root inflammation in combination with periodontitis is the most common cause of tooth loss in adulthood.
Tooth root inflammation can also occur without pain if the nerve is already severely damaged. There is then a risk that the inflammation of the tooth root will become chronic and continue to spread undisturbed. In this case, a swollen jawbone and swollen lymph nodes often provide the first indication.
What effects does tooth root inflammation have on the rest of the body?
Unfortunately, inflammation in the jaw area is not limited to the jaw area. It has now been scientifically confirmed that problems with the teeth can trigger a whole range of serious illnesses. Unrecognised inflammation in the mouth, such as tooth root inflammation, periodontitis or tooth decay (or a combination of these diseases) causes bacteria to accumulate in dead nerve tissue and enter the bloodstream. Via the bloodstream, the bacteria can trigger various diseases throughout the body - from mental illnesses and an increased risk of heart attack to an increased risk of premature births.
Diagnosis: When to see a doctor for root canal inflammation?
In the case of tooth root inflammation, the earlier it is recognised and treated, the better it can heal. If root inflammation is detected at an early stage, the inflammation can be treated without damaging the pulp. If you wait too long, in the worst case you may have to say goodbye to the tooth.
You should therefore make an appointment with your dentist at the first sign of root canal inflammation. The dentist will then examine the affected area thoroughly and usually carry out a tapping test to see how advanced the inflammation is. Using a vitality test, the dentist can determine whether the tooth nerve is still alive or has already died. Specifically, this means that the dentist applies a cold stimulus to the tooth or performs a test drilling. If this does not cause any pain, the nerve is already dead.
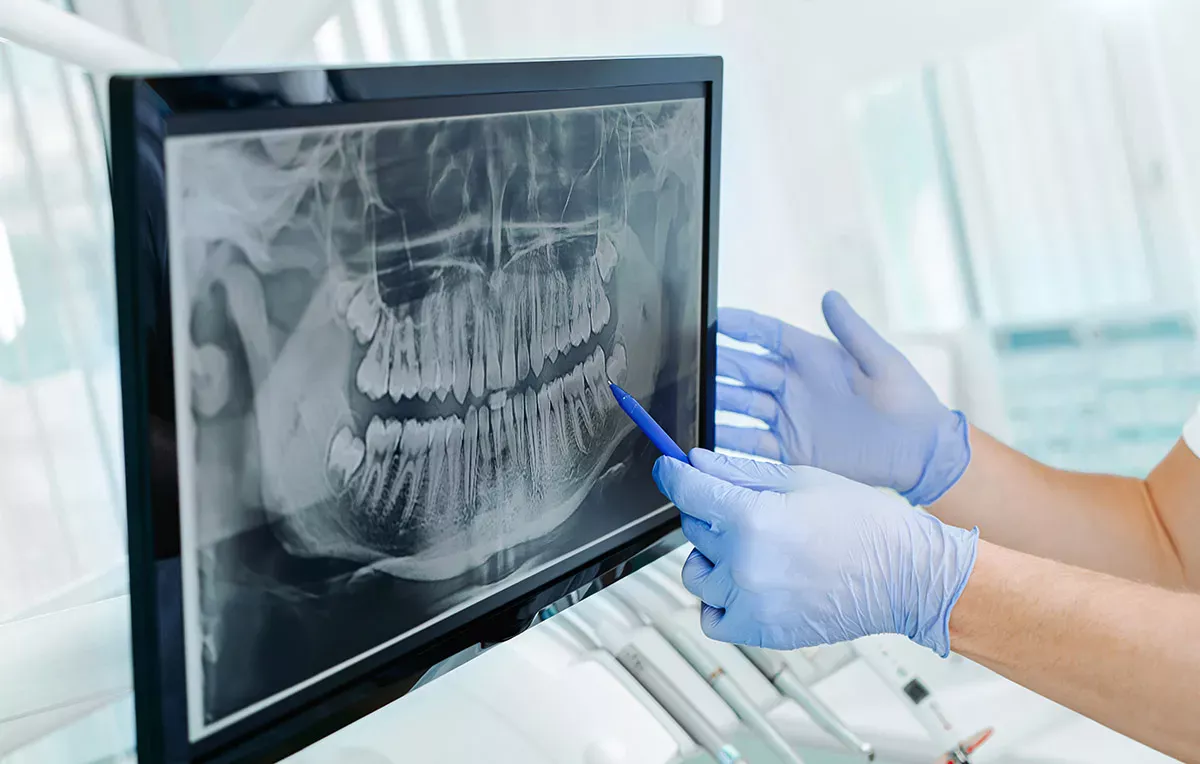
Imaging procedures such as X-rays, computer tomography or 3D volume tomography can also be used to assess the extent of the inflammation.
Treatment: What to do in case of tooth root inflammation?
The treatment of an inflamed tooth root depends on how far the inflammation has progressed. In technical terms, a distinction is made between reversible (reversible) and irreversible pulpitis. The latter can no longer be reversed because the pulp has already been damaged too severely.
Treatment of reversible tooth root inflammation
If root inflammation is reversible, it can often be treated and cured relatively well. As the inflammation is limited, the dentist can easily identify and eliminate the cause of the inflammation. Caries that has reached the pulp is often the cause of reversible root inflammation. In this case, the dentist removes the bacteria and treats the affected area first with a wound dressing and then with a filling. The root inflammation then usually recedes completely.
Treatment of irreversible root canal inflammation: Root canal treatment
The treatment of irreversible tooth root inflammation is more complicated: If the dental pulp is irreversibly damaged, the dentist usually has to resort to root canal treatment. The tooth is drilled out under local anaesthetic and the pulp is completely removed in order to completely eliminate the inflammation. The root canals must also be cleaned with special, very fine files. The inside of the tooth is then rinsed with a disinfectant solution.
To prevent new bacteria from entering, the "empty" inside of the tooth is filled tightly with a natural rubber. However, it must first be ensured that the inflammation has been completely removed. Root canal treatment is therefore often carried out in several sessions. Between sessions, patients wear an insert containing an antibacterial medication. In severe cases, antibiotics may also be used.
Good to know:
Here you can find out exactly how root canal treatment works, what costs you can expect and what you need to bear in mind after the procedure:
Root apex resection
If a root canal-treated tooth becomes inflamed again, which can happen even years after root canal treatment, a root tip resection is a possible form of treatment. This is a surgical procedure in which the dentist removes the inflamed part of the tooth root from the outside. As this procedure cannot be carried out through the tooth, the dentist must first penetrate the gums and jawbone to reach the root tip.
Tooth extraction
In the case of irreversible tooth root inflammation, in addition to root canal treatment, there is also the option of having the tooth extracted and then having a dental prosthesis - for example in the form of an implant - inserted.
Medication: What helps with tooth root inflammation?
You can take an over-the-counter painkiller such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to relieve severe pain and bridge any waiting time for the dentist appointment. Although ibuprofen is anti-inflammatory, it does not treat the cause of the root inflammation. Therefore, you should not rely on an automatic cure with painkillers, but go to the dentist.
After treating the root canal infection, your dentist may prescribe the use of an antibacterial mouthwash with chlorhexidine. Follow your dentist's instructions.
Good to know:
In addition to the antibacterial active ingredient chlorhexidine, the mouthwashes in the Perio plus range from Curaprox also contain Citrox® - a natural active ingredient that enhances the effect of chlorhexidine and is obtained from bitter oranges.
Prevention: How can I prevent root canal inflammation from developing?
You already know that tooth root inflammation is a serious matter because, in the worst case, it can lead to tooth loss or serious illnesses throughout the body. So it's all the better if it doesn't happen in the first place. Proper dental care is the be-all and end-all here. After all, tooth root inflammation is caused by bacteria, which can naturally multiply much more easily with poor dental hygiene. We have collected a few tips for you here on how to look after your teeth properly and minimise the risk of tooth inflammation.
1. Go to the dentist regularly and immediately in case of pain
If your dentist regularly checks your mouth, the likelihood of serious tooth decay and deep periodontitis is significantly lower than if you have avoided the dental practice for years. Your dentist will recognise dental diseases at an early stage and intervene in good time to prevent worse if you attend the recommended check-up appointments. Ideally, you should also have your teeth professionally cleaned once or twice a year to remove tartar - this is where bacteria feel particularly at home.
If you have a toothache, you should make an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible and not wait a few weeks. The longer you wait, the more uncomfortable the treatment is likely to be.
2. Pay attention to a healthy diet
Bacteria love sugar. That's why we learn from an early age that sweets are bad for our teeth. If you minimise the amount of sugar in your diet, your teeth will be happy and you will suffer from root canker sores less often. Expert tip: Instead of snacking on small portions several times a day, you should minimise your sweet cravings and rather eat a sweet dessert after a main meal. That way, your teeth will only be attacked by sugar once. The same also applies to sweet drinks: instead of taking many small sips over a long period of time, it is better for your teeth to drink a glass of juice or lemonade quickly.
Good to know:
Low carb, clean eating, keto diet, vegan diet - there are currently many dietary trends circulating. But what does a healthy diet actually look like?
3. Brush your teeth properly
Last but not least: The most important factor in avoiding dental problems such as tooth root inflammation is regular and thorough brushing twice a day. Ideally, you should brush your teeth after breakfast and before going to bed for about three minutes with a soft toothbrush (e.g. the CS 5460 from Curaprox). Once a day, you should also clean the spaces between your teeth with an interdental brush. Bacteria particularly like to nest in these hard-to-reach areas.
Good to know:
What exactly is the - scientifically proven - most efficient toothbrushing technique? You can find detailed step-by-step instructions here:
Sources
AWMF online: S2k.guideline apicoectomy.
Bolshukhina, Liubov et al.: What is tooth root inflammation?, on: apotheken-umschau.de.
Casa Dentalis: Tooth root inflammation: symptoms and treatment options.
Dentolo: When teeth make you ill: How dental health affects our body.
ECDI (The European Centres for Dental Implantology): Tooth root inflammation.
Gödel, Clemens: Tooth root inflammation, on: netdoktor.de.
National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Dentists: When is a root canal treatment necessary?, How does the treatment proceed?, When is an apicoectomy necessary? and How does an apicoectomy proceed?
Kröplin, Tim: When sick teeth hit the heart, on: zeit.de.
Pirot, Marcus: Does the tooth affect the heart? Tooth inflammation and its effect on the cardiovascular system, on: diakoneo.de.
Zahnarztpraxis Bissfest: Tooth root inflammation: symptoms, causes and treatment.
All websites last accessed on 23/06/2023.
 Swiss premium oral care
Swiss premium oral care