Definition: What are dentures?
The term dental prosthesis refers to any form of dental prosthesis that replaces one or more missing or severely damaged teeth. The aim is, on the one hand, to restore the function of the tooth when chewing and speaking and, on the other hand, to achieve as natural an appearance as possible. Purely cosmetic measures such as veneers are not considered dental prostheses.
Dentures are always used when teeth are missing or severely damaged. This is especially the case with older people. However, teeth can also fall out or have to be extracted due to injuries, diseases such as periodontitis or even after cancer therapy.
Depending on how many teeth are missing or how big the gap is, there are different options:
- Fixed dentures: crowns, bridges and implants
- Removable dentures: full dentures and partial dentures
- Combined dentures: removable dentures plus implants
In the following, we take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages as well as the possible uses of the various options.
Fixed dentures: standard for small to medium gaps
If only a single tooth is damaged or a maximum of four teeth are missing, the dentist can fit a crown or a bridge to close the gap.
Fixed dentures can be made from the following materials:
- Metal: Full metal crowns and bridges are made of metals such as steel or gold. They can last up to 25 years and are mainly used in non-visible areas of the dentition.
- Ceramic: All-ceramic crowns and bridges are closest in appearance to natural teeth and are more expensive than metal crowns. Ceramics are often used especially for incisors where a natural colour is important.
- Resin: All-resin crowns and bridges may discolour after some time and are more prone to plaque formation.
- Mixed forms of metal and ceramic or plastic: Veneered crowns and bridges have a metal framework and are optically matched to the tooth colour by an outer ceramic or plastic layer.
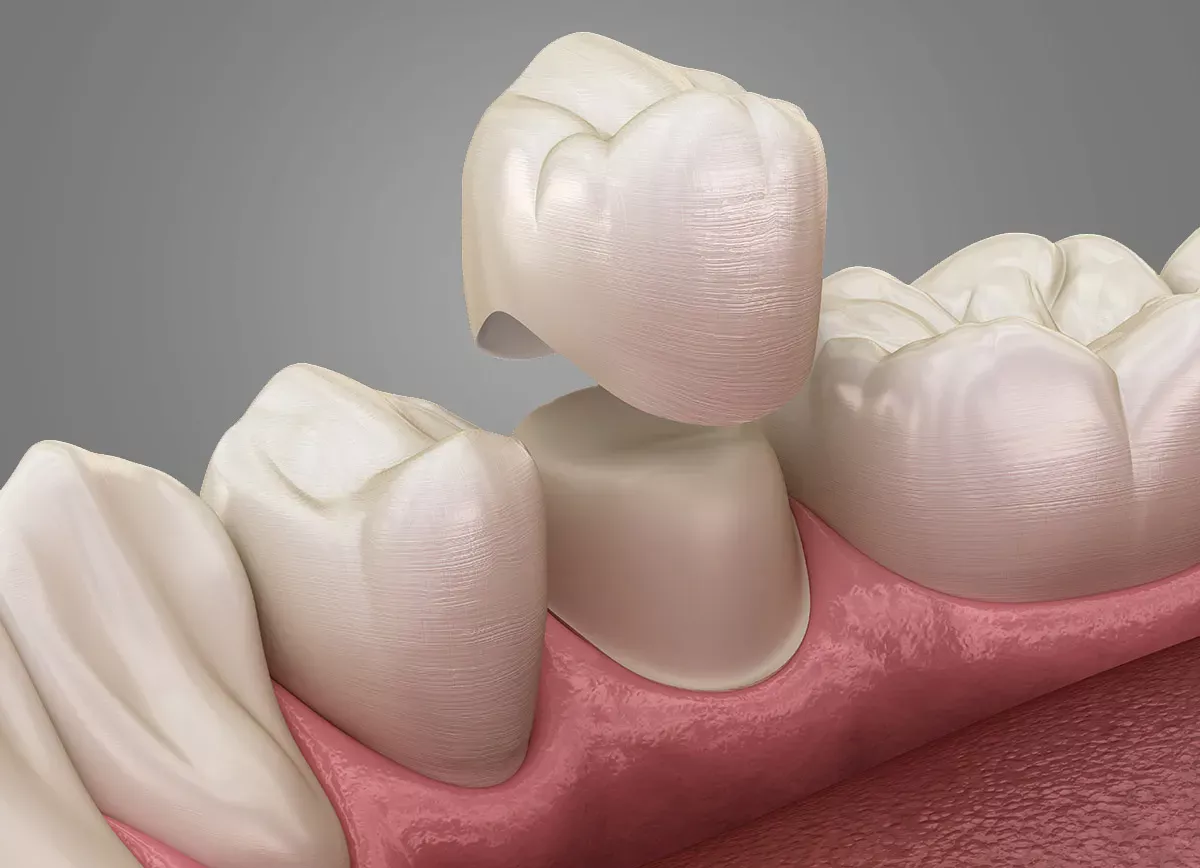
Crowns
If the root of a tooth is intact but the crown is broken off or so badly affected by decay that fillings or inlays are no longer possible, the dentist can fit a crown. To do this, he or she grinds off the affected tooth. A dental technician makes the crown in the laboratory using an impression and then the dentist cements it onto the remaining tooth stump. The crown serves to protect the root of the tooth on the one hand, and on the other hand it ensures that the chewing and speaking functions as well as the appearance of a complete set of teeth are restored. Once it is bonded on, it cannot be removed.
Advantages of crowns:
- Preservation of teeth affected by caries
- Protection against recurrence of caries
- Natural appearance with ceramic, plastic or veneer crowns (especially important for anterior teeth)
- Full functional preservation of the tooth
Disadvantages of crowns:
- Increased plaque formation or discolouration possible with plastic crowns
- Grinding of the tooth necessary
- Limited shelf life (10 to 25 years depending on material)
- Risk of caries due to poor fit at the crown margin
Bridges
If a maximum of four teeth are missing next to each other, a dental bridge is usually the first choice. Depending on the number of missing teeth, the dentist has the dental technician make a bridge with several units. The neighbouring teeth next to the gap serve as supports and have to be ground down to the gum line and crowned - just as described for the crown. In the process, the teeth lose about 40 to 60 per cent of their tooth substance. The two abutment teeth then support the entire bridge. There is no connection between the bridge and the jawbone.
Advantages of bridges:
- Low treatment effort
- Inexpensive alternative to implants
- Tooth gap is closed
Disadvantages of bridges:
- Grinding of neighbouring teeth necessary
- Heavy load on the adjacent teeth
- Short warranty period for crowns (only 2 years in Germany)
- Bone substance at risk
- Risk of caries at the edge of the bridge
- Not very suitable for periodontitis patients
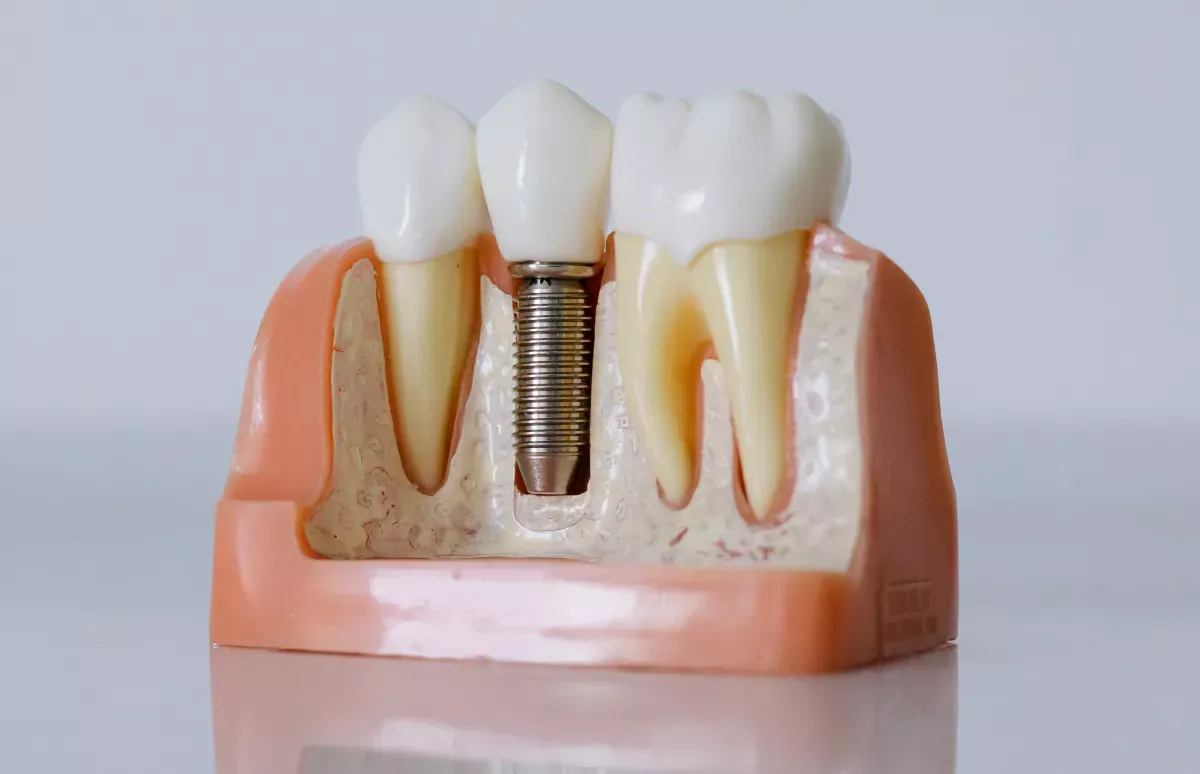
Implants
Implants, when you get right down to it, are not tooth replacements, but rather root replacements. They are metal pins made of titanium that are drilled into the jaw and anchored there - similar in principle to a dowel. Implants are the only type of tooth replacement that have direct contact with the jawbone, thus preventing the bone tissue from regressing. Instead, it wraps itself around the implant surface and ensures a particularly good hold.
A crown, bridge or even a prosthesis can be placed on an implant. With a single tooth implant, the missing tooth is replaced one-to-one by a combination of crown and implant. Implant bridges work like normal bridges; however, they are attached to an implant rather than a healthy neighbouring tooth. Implants are considered the highest quality, most comfortable and most aesthetic form of tooth replacement. However, as they require extensive surgery, they are also the most expensive option.
Advantages of implants
- True replacement for missing tooth through root-like anchorage
- Very good aesthetics
- No grinding of the neighbouring teeth necessary
- Maximum comfort and best support
- Integration in removable prosthesis is possible
- Suitable for people with mild to moderate periodontitis
- No regression of the jaw bones due to anchorage
Disadvantages of implants
- Most expensive dental prosthesis variant
- Surgical intervention is necessary
- Longer treatment time
Dentures are always used when teeth are missing or severely damaged. This is especially the case with older people. However, teeth can also fall out or have to be extracted due to injuries, diseases such as periodontitis or even after cancer therapy.
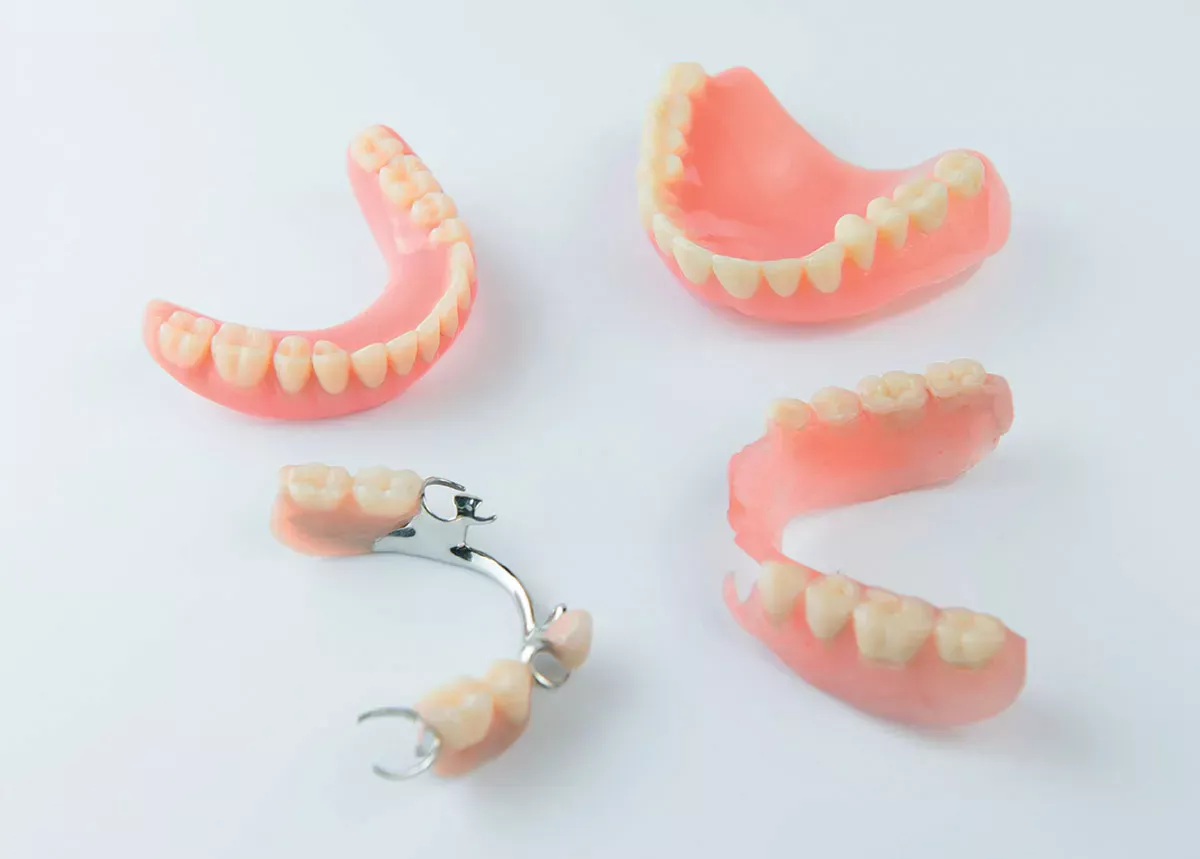
Removable dentures: full and partial dentures
If more than four teeth are missing next to each other, those affected have the choice between implants or removable dentures in the form of prostheses. The dentures are not firmly anchored in the jaw, but can be removed at will, similar to loose braces.
Good to know:
Removable dentures are sometimes not suitable for dementia patients and people with disabilities because the insertion of the denture can lead to difficulties or even be forgotten.
A distinction is made between partial dentures, where there are still remaining teeth in the dentition, and full dentures for a completely toothless dentition. Partial dentures come in different forms: telescopic dentures, clasp dentures or attachment dentures.
Here you will find all the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of removable dentures:
Full denture
The full denture or total denture is used when there are no teeth left in the denture. Dental technicians can make full dentures for both the upper and lower jaw. They replicate the respective part of the jaw with a gum-coloured plastic base with plastic teeth.
Full dentures are not anchored in the jawbone, but are held in place by a suction effect. In the upper jaw, the denture with palatal plate "sticks" to the entire palate, so to speak, and thus has a relatively good hold. In the lower jaw, the contact surface is much smaller and the hold of the denture is therefore much less stable - even with adhesive cream.
Advantages of full dentures
- Inexpensive compared to implants
- No surgical intervention necessary
- No pain during insertion
- Relatively low manufacturing costs
- Natural look for modern models
- Good hold in the upper jaw
Disadvantages of full dentures
- Pressure points and pain due to poor fit
- Taste impairments possible
- Possible psychological stress and restriction of the quality of life
- Low wearing comfort (covering the entire palate, poor hold in the lower jaw)
- Impairment of the chewing function possible
- Regression of the jaw bones possible
- Triggering of gag reflex possible
Clasp prosthesis/model cast prosthesis
The simplest form of partial denture is the clasp denture, also called a model cast denture. A row of acrylic teeth sits in a gum-coloured base and is attached to the remaining teeth via cast steel clasps (or bent wire clasps in the case of a temporary). The aesthetics of the clasps are rather unpopular with patients as they are clearly visible. However, as this is the cheapest type of partial denture, it is still used quite frequently.
Advantages of clasp dentures
- More cost-effective than partial dentures and implants
- No grinding of healthy teeth necessary
- Simple production
- Often expandable
Disadvantages of clasp dentures
- Poor aesthetics due to visible brackets
- Wear of the healthy teeth due to braces
- Possible poor fit and impairment of chewing function
- Pressure points with poor fit
- Regression of the jaw bones possible
Telescopic dentures/telescopic bridges
The more aesthetically pleasing alternative to the clasp denture is the telescopic denture. For this, the dentist grinds down the remaining residual teeth so that they are smooth and cylindrical and serve as a "slot" for the denture. Since the teeth are firmly anchored in the jaw and the prosthesis is firmly attached to the crowns, the telescopic prosthesis offers a better hold and no visible clasps. However, the fabrication is very complex, as the inner crown (the remaining, ground down and crowned tooth) and the outer crown (the prosthesis) have to mesh perfectly.
Due to the increased effort, the telescopic prosthesis is significantly more expensive than the clasp prosthesis. In terms of function, telescopic dentures are similar to bridges; however, they can be removed. For the inner crowns, the ground down remaining teeth are usually covered with gold; the use of white zirconium oxide ceramics is now also possible.
Advantages of telescopic dentures
- Very good hold and clamp-free aesthetics
- Expandable
- Suitable for patients with periodontal disease
Disadvantages of telescopic dentures
- Grinding of healthy teeth necessary
- Heavy loading and accelerated wear of abutment teeth
- Caries risk at the crown margin
- Complex production and high cost factor
- Regression of the jaw bones possible
Attachment prostheses
In principle, an attachment denture works similarly to a clasp denture - but without visible clasps. Instead, denture wearers:inside attach their thirds with a matrix-patrix system: To do this, residual teeth are crowned in such a way that a fastening element is attached to the side or back for which the denture contains the matching counterpart. Due to the exact fit, attachment dentures can ensure a secure hold. This tooth replacement variant was mainly used for molars without an adjacent tooth before implants became more popular.
Advantages of attachment prostheses
- Natural look due to clamp-free aesthetics
- Good hold with full chewing function due to secure anchorage
Disadvantages of attachment prostheses
- Grinding of healthy teeth necessary
- Heavy loading and accelerated wear of abutment teeth
- Not extendable; new fabrication necessary in case of renewed tooth loss
- High manufacturing effort and cost factor
- Regression of the jaw bones possible
Combined dentures
Since the introduction of implants, there are completely new methods of dental prostheses for the lower and upper jaw: when implants are combined with full or partial dentures, they are called combined dentures. Compared to the classic removable denture, combined variants offer a significantly better hold due to the anchoring of the implants in the jawbone and thus also prevent a decline of the bone tissue. Due to the surgical intervention and the more complex production, the cost factor for combined dentures naturally also increases.
In general, the following applies: Even two implants as a supplement to the full denture considerably improve the wearing comfort. However, four or six implants that can support a full or partial denture with different retaining elements are common:
- Denture with push button (locator denture)
- Dentures with implant magnets
- Denture with ball anchor
- Denture with bar prosthesis
- Telescopic bridges on implants
It is also possible to use both remaining teeth and implants as abutments for a prosthesis or bridge. For example, a telescopic prosthesis can be supported by a crowned tooth and an implant. This is called a hybrid denture.
Advantages of combined dentures
- Better hold and higher wearing comfort than with classic removable dentures
- Very good aesthetics
- No grinding of healthy teeth necessary (except for hybrid prosthetics)
Disadvantages of combined dentures
- Higher costs
- Longer treatment duration
- Surgical intervention necessary
Decision factors: Which denture is right for me?
There are many factors that play a role in choosing the right denture:
Medical factors
The most important factor is the medical condition of the dentition. The possible variants depend greatly on how many teeth are still left in the dentition. If only one tooth is missing, a crown or an implant with a crown is the first choice. If up to four teeth are missing, bridges or implant bridges can be considered. If many teeth are already missing, partial dentures or combined dentures are possible options. A completely toothless denture requires a classic full denture or an implant-supported full denture.
Which denture for periodontal disease?
In cases of jawbone loss due to periodontal disease, the condition should be treated before dentures are placed, if possible, to prevent the condition from worsening. Implants are often the best choice for mild to moderate periodontal disease. However, if jawbone atrophy is already present and the density of the jawbones is no longer sufficient to anchor implants securely, removable dentures are a better option.
With a telescopic denture, remaining teeth can support the denture. In case of additional tooth loss, the prosthesis can be reworked. If there is only a small gap and the neighbouring teeth are still firmly in the jaw, bridges are also possible. The question "bridge or implant?" cannot be answered in a general way; it depends on the individual situation.
Important: If you have periodontitis, the risk of peri-implantitis - an inflammation of the periodontium at the implant site - is five to seven times higher after the insertion of implants than in healthy patients.
Peri-implantitis: What to do about inflammation around an implant?
Aesthetics and wearing comfort
If you attach great importance to aesthetics and a natural denture that is as inconspicuous as possible, implants or a telescopic denture are the best choice. Since implants are firmly anchored in the jawbone, there is no danger of the denture falling out or slipping. Chewing and speaking functions are the same as with the original teeth.
Costs
In general, the dental prosthesis solutions with the best aesthetics and the highest wearing comfort also have the highest cost factor. Since health insurance companies usually only pay a portion of the costs, patients must carefully consider how much they want to invest in their dentures and how important optimal aesthetics are to them. It's best to get advice from different dentists and get several offers for comparison.
Risks of dentures
One thing in advance: If a tooth is lost, it must be replaced. Otherwise, the jaw and bite may shift because there is no longer a counterpart for the opposite tooth. Jaw misalignments can lead to tension and headaches - not to mention the psychological strain of a tooth gap.
Nevertheless, dentures also entail risks:
- Removable dentures can cause pressure points, gingivitis and injuries in the mouth.
- With implants, insufficient care can lead to peri-implant mucositis - inflammation of the gums around the implant - or peri-implantitis. In the worst case, this leads to the loss of the implant.
- Caries can form at crown edges.
- If removable dentures are not cleaned properly, fungi and bacteria can take hold and thus infect healthy teeth and cause bad breath.
Good to know:
Infections around the implant can be prevented by using a mouth rinse containing chlorhexidine. Immediately before and after implant surgery, the mouthwashes in the Perio plus range from Curaprox can protect against bacterial infection while accelerating wound healing. The natural active ingredient Citrox®, an extract from bitter orange, further enhances the antibacterial effect of chlorhexidine.
The correct care of dentures
To prevent undesirable complications such as gingivitis or caries from occurring with dentures, particularly thorough oral hygiene is the be-all and end-all.
Cleaning of fixed dentures
You should clean bridges, crowns and implants just as thoroughly as your real teeth. You should brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush at least twice a day for at least three minutes. You should also clean your teeth and implants daily with an interdental brush.
Here we have compiled some articles with helpful tips on how to brush your teeth properly:
Instructions: Brush your teeth properly
Instructions: Brushing your teeth with an electric toothbrush
Instructions: Use the interdental brush correctly
Instructions: Use the tongue scraper correctly
Good to know:
There are special interdental brushes for cleaning the spaces between teeth with implants: the bristles of the CPS Soft Implant from Curaprox are larger than those of conventional interdental brushes so that the larger spaces can be cleaned thoroughly and gently. It's best to ask your dentist for advice on which size is best for you.
Cleaning implants with the Single-Brush
To ensure that there is no inflammation around the implant that could develop into peri-implantitis, you can use a single tuft brush for an extra thorough cleaning. Work gently along the gum line in small circular motions. This will help you reach even the hard-to-reach areas under the implant.
Good to know:
The single tuft toothbrush CS 708 Implant from Curaprox has been specially developed for particularly thorough cleaning of implants and has a flexible brush head with which you can easily reach every spot.
Cleaning of removable dentures
When you think of cleaning dentures, you probably have a picture of dentures in a glass of water with a fizzy tablet right in front of your eyes. However, if you think that the overnight effervescent bath is enough, you are sadly mistaken: partial and full dentures need to be brushed just like real teeth. After all, plaque builds up here too. If this is not removed, it hardens into tartar and attacks the denture. In addition, the bacteria cause bad breath and make the dentures less comfortable to wear.
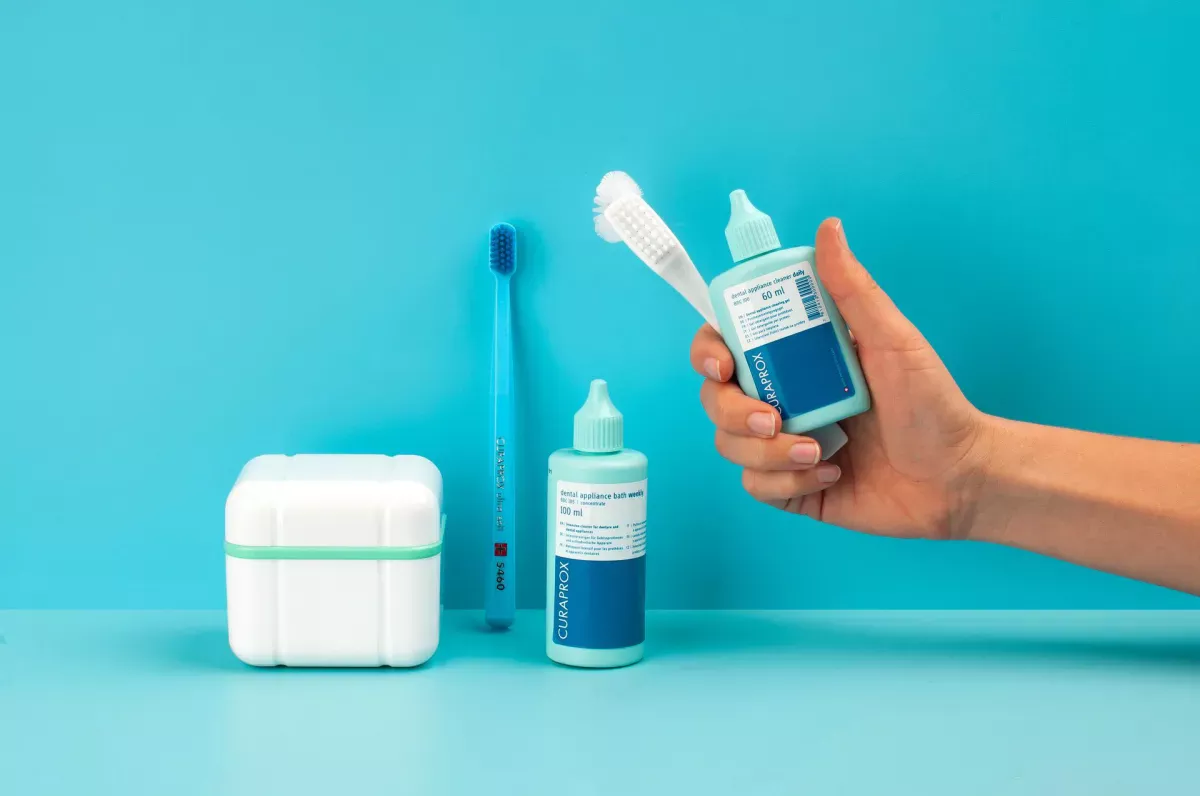
It is best to clean your dentures thoroughly at night before going to bed with a denture brush such as the Curaprox BDC 152 and a special cleaning gel such as the BDC 100. Make sure that you clean all sides of the denture and also clean the inner surfaces. Denture brushes are shaped so that you can reach every part of your denture. Once a week, you should also disinfect your removable dentures with a special disinfectant such as BDC 105. If you want to wear your dentures at night, you should also clean them in the morning - just like your real teeth.
Can dentures be cleaned with ultrasound?
Ultrasonic devices can loosen stubborn deposits. However, you still need to use a denture brush to thoroughly remove the deposits. An ultrasonic device is also used during a professional dental cleaning at the dentist. In addition, your denture will be polished and sealed so that deposits cannot stick so quickly.
Good to know:
The Curaprox cleaning set contains everything you need to clean your removable dentures: daily cleaning gel, denture brush, weekly disinfectant, storage box and instructions - and as an extra, the CS 5460 super-soft toothbrush for massaging the gums.
FAQ: Further questions on the subject of dentures
Dentures are a complex subject. That's why we have answered some common questions here:
Are there dentures for children?
Yes, children can also need dentures if, for example, they lose teeth in a fall or due to severe caries or suffer from a disposition disorder in which the milk teeth do not form. It is important for the healthy development of the child that the gaps between the teeth do not remain empty so that the dentition develops normally and there is no malocclusion or speech disorders.
However, there are fewer options for dentures in children than in adults. Fixed dentures are out of the question because the jaw bones are not yet fully developed. However, so-called "gap retainers" are possible, which are anchored to adjacent teeth with clasps, or removable clasp dentures.
Which is better - plastic or ceramic?
For fixed dentures, ceramic is considered to be of higher quality because it does not discolour as quickly as plastic. However, ceramic is also more expensive. Removable dentures are usually made of plastic. Only the inner crowns of telescopic dentures can be made of ceramic.
Are there dentures without metal?
Yes, for fixed dentures you can choose between metal, ceramic and plastic. Removable dentures are usually made of plastic. Only the clasps of clasp dentures are made of metal. For telescopic dentures, it is possible to have the inner crowns made of ceramic. Full dentures are usually made entirely of plastic. Implants, however, are made of titanium.
Are there dentures from the 3D printer?
Yes, some dental laboratories use 3D printers for the fabrication of dentures and can thus speed up the manufacturing process.
What are the options for dentures without impressions?
Anyone who has ever had to take an impression at the dentist knows how unpleasant this can be. Fortunately, there is now the option of using a digital scan with an intraoral scanner instead, which assembles a digital, three-dimensional image.
Which dentures for osteoporosis?
In principle, all types of dental prostheses are possible in osteoporosis - also known as bone loss. However, the dentist should clarify in the consultation how far the disease has progressed and what medication is being taken. Especially drugs of the bisphosphonate class can cause complications during dental treatment and hinder wound healing. This is especially relevant for implants. In rare cases, bisphosphonates can even trigger jaw necrosis, in which a jaw bone is softened and destroyed.
Good to know:
A poorly fitting denture can be the first sign of osteoporosis. When jaw bones slowly recede, the denture may no longer fit as it used to. Many patients only realise that they have osteoporosis in this way.
When do you need dentures?
It is not possible to say in general terms when a person needs dentures. It depends entirely on how well the person has taken care of their teeth. There is no such thing as purely age-related tooth loss. People who take particularly good care of their teeth can keep their natural teeth well into old age.
How often do you have to reline removable dentures?
To ensure that removable dentures fit well in the long term, the dentist must check dentures regularly - ideally every six months - and reline them if necessary. The jaw bones change over time and it is therefore normal that the denture no longer fits ideally after a while. Since a bad fit can cause pressure points to form, you should definitely go to the dentist to find out if a reline is necessary. The dentist or dental technician simply adjusts the denture base to the new jaw shape.
Can I make dentures myself?
No, please don't. Even though there are numerous offers for DIY kits on the internet that promise instant dentures without a dentist, this is not a real alternative to professional dentures. To ensure that your dentures are aesthetically pleasing, comfortable and functional, you should leave them to the professionals. If your dentures are damaged, you should not repair or glue them yourself. The adhesive can damage the oral mucosa and a poorly bonded denture can lead to poor wearing comfort.
Can I whiten dentures?
Dentures made of plastic can discolour over time - especially if you drink a lot of coffee and tea or smoke. However, you should keep your hands off household remedies such as baking soda, vinegar essence and aggressive toothpaste because they can damage your dentures. It is better to have your teeth professionally cleaned by a dentist. It is even better to avoid severe discolouration by brushing daily and disinfecting weekly.
Sources
Dahm, Valeria: Dentures, on: netdoktor.de.
Dentolo: Your dental prosthesis: bridge, implant & co. at a glance.
Dentnet: Locator dentures - removable dentures with a click.
Dörr, Rebecca: Brightening dentures: Die besten Tipps und Tricks, at: praxistipps.focus.de.
Federal Joint Committee: Dental prosthesis guideline.
informedhealthonline.org: Forms of dentures.
National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Dentists: Types of partial dentures.
Revierkind: Do children need dentures?.
Verbraucherzentrale NRW: Brücke, Krone, Implantat: Welche Unterschiede gibt es beim Zahnersatz?, on: kostenfalle-zahn.de.
Wehner, Christian: Peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, on: zwp-online.info.
Dental practice Dr. Langenbach: Dentures in everyday life - cleaning, storage and care.
ZWP: Osteoporosis and dental prostheses: What patients should bear in mind.
ZWP: Dentures: Think about relining in time.
All websites last accessed on 11.07.2023.
 Swiss premium oral care
Swiss premium oral care