What is the keto diet?
If you're interested in fitness and healthy eating, it's hard to avoid the term keto diet these days. The diet trend is presented on various social media channels, on fitness blogs and in numerous books. However, the ketogenic diet is not a new invention. Back in 1921, a doctor in the USA developed this strict form of nutrition to treat epilepsy - and it is still used today. Nowadays, more and more healthy people are following the keto diet - mainly to lose weight. But what exactly is keto?
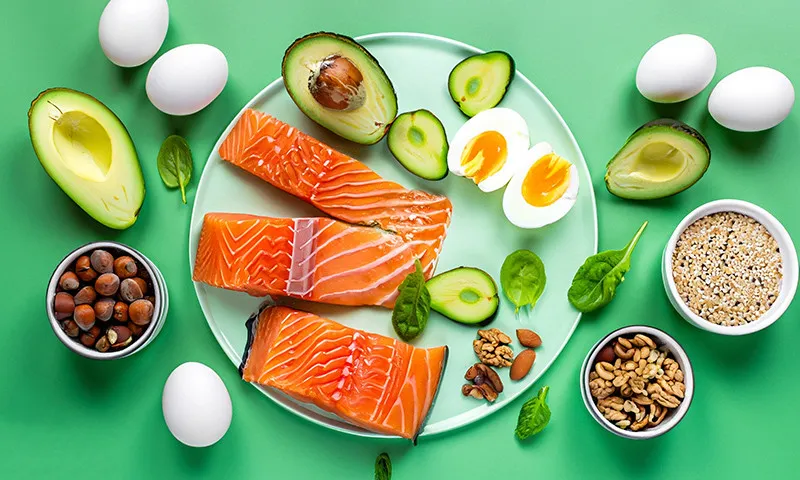
In the ketogenic diet, the ideal distribution of macronutrients is very different to the mixed diet recommended by many institutional organisations. In the keto diet, the diet should consist of around 80 to 85 per cent fat, 10 to 15 per cent protein and only 5 per cent carbohydrates. For comparison: The German Nutrition Society (DGE) recommends that at least 50 per cent of our diet should consist of carbohydrates. You're probably wondering now: What is the benefit of giving up carbohydrates? To answer this, we need to take a closer look at the human metabolism and clarify the meaning of the words "ketogenic" and "keto".
The basis of the keto diet: ketosis & ketones
The aim of the keto diet is to switch the metabolism so that the body no longer draws its energy from carbohydrates, but from so-called ketones (also known as ketone bodies), which are produced from fat in the liver. Both the body's own fats and fats obtained from food are utilised. This process is called ketosis - hence the name keto diet or ketogenic diet.
But what exactly is ketosis? Firstly, let's take a look at the "normal" metabolism:
In a conventional mixed diet, the human body draws energy primarily from carbohydrates. Glucose (also known as dextrose) can either occur directly in carbohydrate-rich foods or be incorporated into complex carbohydrates (for example in wholemeal bread or potatoes). During the metabolic process, glucose is broken down and converted into glycogen and stored in this form in the liver and muscles. If there is too much glucose in the body, the body stores it in the form of fat.
If we eat no or very few carbohydrates, the body switches its metabolism: Firstly, it uses up the free glucose in the blood, then the glycogen stored in the liver and muscles. Then it goes to the fat stores. To obtain energy, the liver converts fatty acids into ketones, which are recognised by all cells as a source of energy. This mechanism of the human body was probably originally intended to ensure survival even when food was scarce. A state of ketosis can also be achieved by fasting. As the body's own fat is burnt during ketosis, many people use the ketogenic diet to lose weight.
Is ketosis dangerous?
No, ketosis is not dangerous, but a normal bodily function that is also activated during fasting - which has been scientifically proven to have numerous health benefits. Important to know: Ketosis does not set in immediately. The body needs a few days to make the switch, during which time side effects can also occur (more on this in the section "Short-term side effects").
The keto diet is the subject of controversial debate among experts: Many doctors and nutritionists consider it to be too one-sided and rather harmful to health, while there are already studies that show positive effects on health. While most experts only recommend the keto diet - if at all - for a maximum period of eight weeks, there are already numerous committed followers who have been following the ketogenic diet for years - including doctors - and have not noticed any negative long-term effects. As you can see, the scientific situation has not yet been clarified.
Keto diet plan: What can I eat on the keto diet?
Now that you know the theory and background, let's take a look at what the actual implementation looks like. In other words, what are you actually allowed to eat on the keto diet? As you already know, you will have to eliminate most carbohydrates from your diet on the keto diet. So you will have to say goodbye to bread, pasta, pizza and potatoes. If you now think that the keto diet only consists of butter and bacon, you're wrong.
Here we have put together the foods you can eat on a ketogenic diet - as well as a few tips and inspiration for your diet plan. An important note at this point: it's best to speak to a specialist (e.g. a nutritionist or doctor) before starting the ketogenic diet. As this form of nutrition is very restrictive, many experts recommend that it should take place under medical supervision. We are only providing tips and recommendations here, which cannot replace medical advice.
Fish and seafood
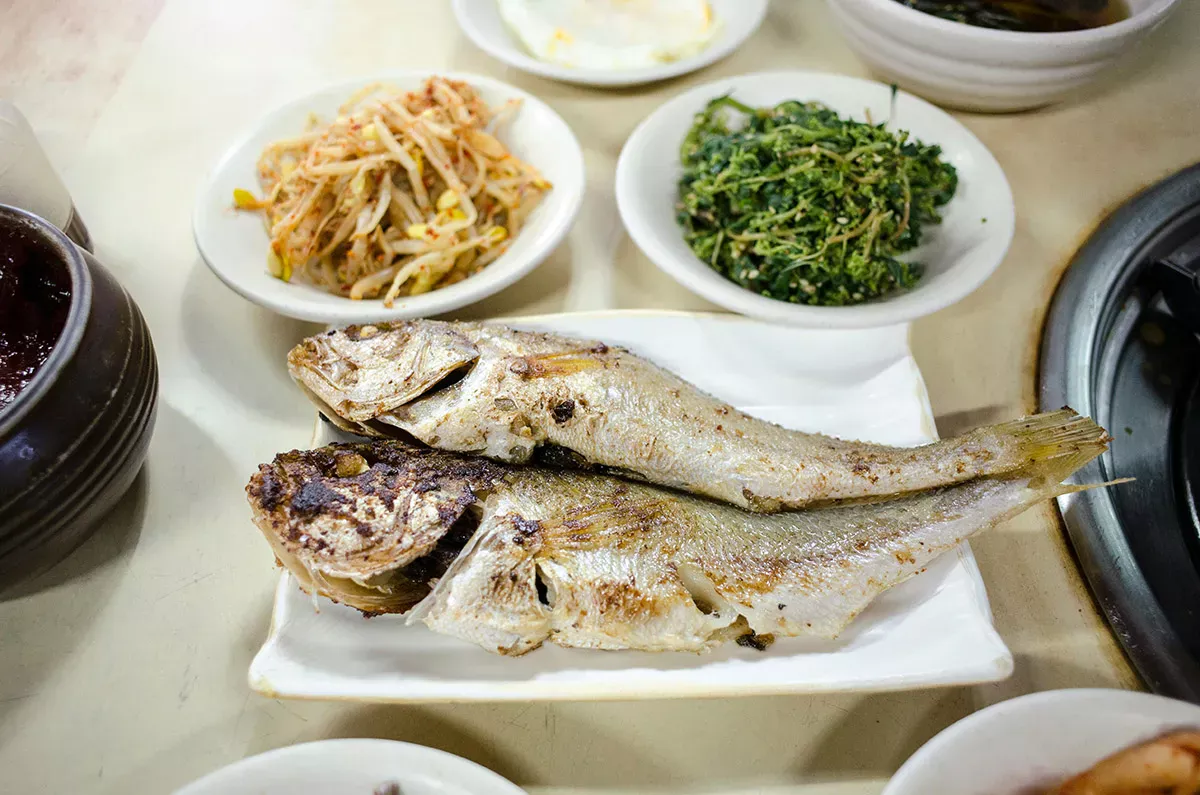
The keto diet favours fatty fish such as salmon, herring and mackerel, which contain virtually no carbohydrates and are also rich in vitamin B, potassium and selenium. Shrimps and crabs are also carbohydrate-free, but other seafood such as oysters or squid contain carbohydrates, which must also be tracked on a strict keto diet to keep you in ketosis.
Meat
Meat provides our body with protein and B vitamins. In order to achieve the desired fat content, you should focus on high-fat meat such as ribeye steak, neck steak, pork belly, bacon or minced meat in the keto diet. In principle, however, all forms of unprocessed meat are permitted, as they contain no carbohydrates. If you want to eat sausage products such as salami, ham or sausages, you should check whether they contain carbohydrates (e.g. sugar or starch). In principle, unprocessed meat is healthier - preferably pasture-raised or organic.
Meat consumption is currently a controversial topic: many nutritionists are critical of increased meat consumption as it contradicts the guidelines of organisations such as the German Nutrition Society. The general recommendation is not to consume more than 300 grams of meat per week. However, there are also scientific studies that prove the positive effects of high meat consumption - even from the "Carnivore Diet", a particularly restrictive sub-form of the keto diet in which people eat only meat. The scientific situation is therefore still unclear and the long-term effects of very high meat consumption have not yet been researched.
Eggs
One egg contains less than one gram of carbohydrates, about six grams of protein and about 5 grams of fat. Eggs are therefore well suited to the keto diet. They also contain all essential amino acids and all vitamins except vitamin C.
Dairy products
When it comes to dairy products, official institutions and the keto diet agree: dairy products are good for the body. Cheese, butter, cream, Greek yoghurt and the like not only contain fat, but also calcium to strengthen bones and teeth. In contrast to other diets, you should primarily opt for the high-fat varieties - low-fat light versions are not ketogenic and could even throw you out of ketosis.
The following dairy products, among others, are suitable for the ketogenic diet:
- Brie
- Camembert
- Gorgonzola
- Mozzarella
- Feta cheese
- Harz cheese
- Parmesan cheese
- Gouda cheese
- Cottage cheese
- Quark
- Greek yoghurt
- Mascarpone
- Ricotta
- Whole milk
- Cream
- Sour cream/sour cream
Please note: dairy products contain lactose, which is converted into glucose in the body. You must therefore also track the carbohydrate content of dairy products and should not consume too much so that you can also eat enough vegetables. As an estimate: 100 grams of whole milk contain five grams of carbohydrates.
Low carbohydrate vegetables
Even if your diet consists largely of fat, that doesn't mean you can't eat a crisp salad. Water-rich leafy and cabbage vegetables provide you with vitamins and minerals and conjure up volume on your plate.Despite a strict carbohydrate limit, you 900 grams of vegetablesa day- but the choice is limited
The following vegetables should be plentiful on the keto plate:
- Green salad
- Cucumber
- Leek
- Courgette
- Mushrooms
- Aubergine
- Paprika
- Jalapeños
- Celeriac
- Pak Choi
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Chinese cabbage
- Brussels sprouts
- White cabbage
- Kale
- Spinach
- Artichoke
- Asparagus
Many keto followers use low-carb vegetables to make alternatives to the usual side dishes: courgettes cut into very thin strips are used as a substitute for spaghetti. Grated cauliflower is used as a rice substitute and mashed cauliflower as an alternative to mashed potatoes.
Many other vegetables have a slightly higher carbohydrate content, but can be used as long as you track the carbohydrates and do not exceed 50 grams. These include onions, garlic, tomatoes and carrots, for example. In general, vegetables that taste sweet or grow underground usually have more carbohydrates than leafy and cabbage vegetables. Salt, pepper, spices and herbs are also permitted in the keto diet.
Most types of fruit contain too much sugar and are therefore not suitable for the keto diet. However, you don't have to give up fruit completely: Berries contain few carbohydrates and provide the body with vitamins and antioxidants that protect against inflammation. Lemons, limes and papaya are also allowed.
Permitted are:
- Strawberries
- Raspberries
- Blueberries
- Currants
- Cranberries
- Blackberries
- Gooseberries
- Papaya
- Lemons
- Limes
Two other types of fruit that are essential for a ketogenic diet, but are not directly associated with fruit by most people, are olives and avocados. Both types of fruit have a high fat content.
Oils and fats
Medium chain triglycerides (MCT fats) are particularly suitable for the ketogenic diet because the body can convert them into ketones particularly quickly. These fats occur naturally in coconut oil. Special MCT oil is a popular dietary supplement for the keto diet, which consists exclusively of easily metabolisable MCT fats.
Olive oil has numerous positive effects on health and can be used in abundance on the keto diet. Avocado oil is also a good choice. In addition to vegetable oils, you can also use animal fats such as lard. Lard has been used for centuries in Indian cuisine under the name "ghee" and is also very popular among keto followers. This is clarified butter, which is also suitable for frying.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts are a nutrient-rich source of fat that supplies our body with omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and important minerals.
The following nuts and seeds are permitted on the keto diet:
- Almonds
- Hazelnuts
- Walnuts
- Cashew nuts
- Pistachios
- Macadamia nuts
- Pecan nuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Hemp seeds
- Linseed
- Chia seeds
- Sesame
- Pumpkin seeds
You can also use many of these seeds and nuts in ground form for baking - for example almond flour and pumpkin seed flour.
Drinks
As sugar is taboo on the keto diet, sweet drinks such as lemonades, juices and soft drinks are immediately eliminated. Coffee, unsweetened tea and water are allowed. For all other drinks - for example flavoured water - you need to track the carbohydrate content.
Bulletproof coffee - black coffee with butter and MCT oil - is particularly popular with followers of the keto diet. This rich drink in the morning is said to keep you full for a long time and increase concentration.
Cocoa and chocolate
After all the restrictions, there is a surprise: chocolate is not completely off the table, it only has to contain more than 70 per cent cocoa. Baking cocoa is also allowed - for baking or in quark or Greek yoghurt, for example.
How many carbohydrates are allowed on the keto diet?
The carbohydrate limit for the ketogenic diet is between 15 and 50 grams. If you want to get into ketosis as quickly as possible, you can drastically reduce your carbohydrate intake to up to 15 grams; for a longer keto diet, you can consume up to a maximum of 50 grams of carbohydrates per day. Important: Carbohydrates should mainly consist of complex carbohydrates from vegetables, berries and dairy products. You should completely eliminate sugar from your diet when following the keto diet.
Which foods do you have to avoid on the keto diet?
Although the list of permitted foods in the ketogenic diet is relatively long, there are numerous foods that you will search for in vain.
The following foods are taboo on the keto diet:
- Sugar in any form (for example white sugar, brown sugar, honey, agave syrup and maple syrup - exception: erythritol is permitted in small quantities)
- Sweet fruit (for example apples, bananas, dates, oranges and tropical fruit such as pineapple and mango)
- Cereal products (for example bread, pasta, pizza, rice, couscous and sweet pastries, but also quinoa)
- Starchy vegetables (for example potatoes and sweet potatoes)
- Pulses (for example beans and lentils, but also peanuts)
- Carbohydrate-heavy convenience products (e.g. crisps, frozen pizza, biscuits and sweets, but also dressings and sauces)
- Sweet drinks (e.g. cola, lemonade and other soft drinks, but also alcoholic drinks)
What is the difference between keto and low carb?
The keto diet is a particularly strict sub-form of the low-carb diet. While "low carb" is about eating few carbohydrates, the goal is not necessarily ketosis. The low carb diet is much more flexible and allows fruit and vegetables, which are not included in the keto diet. There is no strict carbohydrate limit on the low-carb diet. If you want to lose weight, you usually achieve this through a calorie deficit and not through ketosis.
Inspiration for your keto nutrition plan
Here are a few delicious dishes that adhere to the strict rules of the keto diet:
Breakfast
One of the advantages of the keto diet is that ketosis suppresses the feeling of hunger. Many followers of the keto diet either don't eat breakfast at all or drink a bulletproof coffee - i.e. black coffee with butter and MCT oil. However, if you do want to eat something in the morning, you can reach for eggs or cottage cheese, for example:
- Omelette fried in ghee/butter lard with avocado and cucumber
- Fried eggs with bacon in olive oil
- Scrambled eggs with feta and olives
- Eggs baked in avocado halves with ham or smoked salmon
- Cottage cheese with peppers, olives and fresh basil
- Greek yoghurt with berries and nuts
Lunch and dinner
As bread is taboo in the keto diet, the classic evening meal is omitted. Instead, you can also eat a warm meal or salad in the evening. A standard meal in the keto diet should consist of low-carb vegetables and a high-quality source of fat and protein. Here are a few examples for inspiration:
- Salmon fried in olive oil with asparagus
- Ribeye steak fried in clarified butter with broccoli
- Oven-baked vegetables with feta and chicken thighs baked in olive oil
- Green salad with tuna, egg, avocado, olives, oregano, olive oil and a little lemon juice
- Minced meat and white cabbage casserole
- Cheese and leek soup with minced meat
- Peppers stuffed with minced meat and baked with cheese
- Sliced turkey with mushrooms and cauliflower rice
- Chicken and vegetable pan with olives, courgettes, aubergines, peppers and Parmesan cheese
Dessert
Although you have to avoid sugar on a ketogenic diet, this does not mean that you can no longer eat desserts. Here are a few examples:
- Keto brownies with dark chocolate, almond flour, eggs and butter
- Chocolate mousse with eggs and dark chocolate
- Homemade keto ice cream
- "Fat Bombs" with ground and chopped nuts, coconut oil, dark chocolate and baking cocoa
- Greek yoghurt with nut butter and cocoa
Snacks
If you get a little hungry and need to bridge the gap until your next meal, you can use the following snacks on the keto diet:
- A handful of nuts
- Turkey breast rolls with cream cheese
- Greek yoghurt with nuts and cinnamon or berries
- Olives
- Dark chocolate (at least 70% cocoa content)
- Pepper strips with avocado dip
- Cottage cheese with berries
What do you need to look out for on a ketogenic diet?
As you already know, the keto diet requires you to eliminate a lot of foods from your diet. To ensure that you still provide your body with all the important vitamins and minerals, you should make sure you eat enough vegetables, berries and nuts. Even if you have to stick to a very strict carbohydrate limit, you should try to make your diet as varied as possible with salads and low-carb vegetables. In the next section you will find a few ideas for a colourful keto diet plan.
When choosing food, pay particular attention to quality and freshness. Unprocessed organic meat and fresh vegetables are much healthier and contain more vitamins and nutrients than tinned vegetables and sausages. The same applies to the choice of fats: pay attention to quality and healthy, unsaturated fatty acids. That's why your diet should mainly include high-quality, fatty foods such as avocados, olive and coconut oil, meat, fish and nuts.
Good to know:
Fancy some healthy snacks? You'll find plenty of inspiration in our article:
Tips for switching to the keto diet
Although you don't have to count calories on the keto diet, you do have to count carbohydrates. That's why you should inform yourself well before the changeover and plan your meals so that you are not overwhelmed during the changeover itself. Think about which foods you like to eat and how you can integrate them into your keto diet plan. It's best to put together a diet plan for the first few weeks and distribute the carbohydrates accordingly. You can also try out a less strict low-carb diet at first and slowly reduce the proportion of carbohydrates.
However, you only really reach ketosis when you drastically reduce your carbohydrate intake. Cheating is not allowed on the keto diet. While with other diets you have simply consumed a few too many calories if you slip up, with the keto diet you are jeopardising ketosis. If you consume more than 50 grams of carbohydrates, the body switches back to its normal metabolic mode.
It is certainly helpful to prepare your meals at home when you are first making the switch. Once you have a better sense of how many carbohydrates are contained in which foods, you can also eat in restaurants. Many restaurants offer meat or fish dishes with a side of vegetables. Just ask if you can get more vegetables instead if there is a side dish containing carbohydrates.
Health advantages and disadvantages: Is the keto diet healthy?
So, now you know how the keto diet works. But is keto healthy? Opinions are divided on this question. Unfortunately, it is not yet clear whether the ketogenic diet is healthy. On the one hand, there are already numerous scientific studies that point to positive effects on health. On the other hand, the metabolic change is accompanied by some side effects and the long-term effects have not yet been sufficiently researched. Here we first present the health benefits and then the criticism of the ketogenic diet.
Health benefits of the keto diet
Although it is rejected by many doctors and nutritionists, there are already some scientific studies that point to positive effects on health. Here is an overview:
Lose weight with the keto diet
Many people start the keto diet because they want to lose weight. The ketogenic diet can actually help with this. Especially at the beginning, the pounds fall off very quickly because the body first empties all carbohydrate stores. The water released in the process is flushed out via the kidneys. As you already know, on a ketogenic diet our body converts fat reserves (and of course fat from food) into ketones and uses them as a source of energy. This means that the body's own fat is burned during ketosis, which can help you lose weight. Some studies already indicate that the keto diet is more effective for weight loss than the conventional low-fat diet, which primarily avoids fat. However, longer-term studies have shown only a slight difference.
Keto followers also report that they are less hungry as a result of the metabolic change and feel fuller for longer due to the increased protein intake. The ketogenic diet can also help with lipoedema. This is a fat distribution disorder in which large fat cells are deposited on the legs, hips and buttocks. The keto diet can convert these fat cells into energy. In addition, lipoedema is often accompanied by water retention, which can be flushed out on the keto diet.
However, experts warn against the yo-yo effect. Anyone who follows the keto diet for a short period of time and then switches back to their usual - possibly high-sugar - diet runs the risk of rapidly gaining weight again. It therefore makes sense to continue eating a healthy diet even after the keto diet.
Good to know:
What exactly does a healthy diet look like? You can find all the information here:
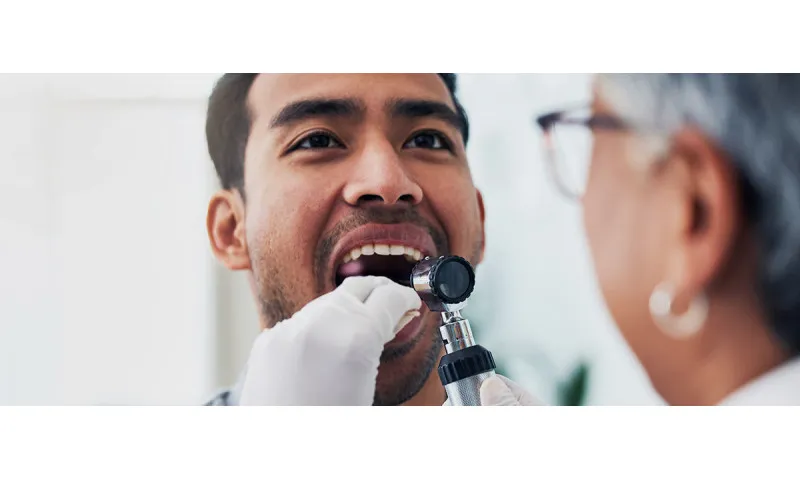
Keto diet and dental health
It should come as no surprise that a diet that completely avoids sugar is good for your teeth. A study by BMC Oral Health has actually confirmed this. The keto diet reduces the risk of tooth decay and gum inflammation, as no acidic fruit, soft drinks or sweets are consumed. The ketogenic diet is therefore definitely beneficial for the teeth.
However, despite the lower risk of dental disease, you should not skip dental care on the keto diet! Some followers of the keto diet post on social media that their oral health has become so good thanks to the keto diet that they no longer need to brush their teeth. However, this is very bad advice. Even if we don't eat sugar, we still need to brush our teeth twice a day and clean the spaces between our teeth every day. Otherwise, your dental health can quickly deteriorate.
Good to know:
Did you know that a soft toothbrush cleans much more thoroughly than a hard one? A densely packed brush head with as many bristles as possible is ideal. Curaprox toothbrushes have been recommended by dentists all over the world for more than 40 years.
Keto diet for diabetes and Alzheimer's disease
Some scientific studies already point to the positive effects of the keto diet on diabetes. For all these diseases, it is important that those affected follow the ketogenic diet under medical supervision, as the insulin intake must be adjusted.
Type 2 diabetes
As hardly any carbohydrates are eaten on the keto diet, blood sugar levels no longer fluctuate greatly, but remain constantly low. This also improves insulin sensitivity. This is particularly important for type 2 diabetics: with this disease, the cells become resistant to insulin, meaning that sugar absorbed through food cannot be broken down. Patients then have to take medication to compensate. The ketogenic diet has several advantages for this condition: on the one hand, significantly less insulin is required due to the greatly reduced intake of carbohydrates, and on the other hand, insulin resistance is significantly reduced, meaning that many type 2 diabetics can stop taking their medication when following a ketogenic diet. Weight reduction is also crucial in this context - obesity is one of the main risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is the preliminary stage of type 2 diabetes, where those affected already have an elevated fasting blood sugar and impaired glucose tolerance, but do not yet have fully developed diabetes. Prediabetes mainly occurs in people who are very overweight. In addition to exercise and a calorie-reduced diet, a ketogenic diet or a less strict low-carb diet is an effective intervention.
Good to know:
You can find out exactly what prediabetes is and what you can do to prevent it here:
Type 1 diabetes
People with type 1 diabetes suffer from an autoimmune disease in which the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas are attacked so that the body cannot produce enough or any insulin to break down sugar. Type 1 diabetics must therefore inject insulin daily. Here, too, there are some studies that indicate that the ketogenic diet can be beneficial because blood sugar levels normalise, significantly less insulin needs to be injected and quality of life improves. Testimonials on the internet also confirm these results. However, the ketogenic diet for diabetics is still controversial among experts and the evidence base is very thin.
Particularly important for type 1 diabetics: while ketosis is harmless, ketoacidosis can be life-threatening. This is an over-acidification of the blood due to a severe insulin deficiency. Ketones are also released here - but to a much greater extent than in ketosis.
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's patients suffer from insulin resistance in the brain. This means that the brain cells cannot absorb blood sugar. The ketones produced by fat cells during ketosis could provide an alternative source of energy and strengthen weakened cells - however, cells that are already damaged cannot be regenerated. Some experts already recommend the ketogenic diet for Alzheimer's patients. Whether it can even have a preventative effect against Alzheimer's is still being researched.
Ketogenic diet for epilepsy
In contrast to the diseases already mentioned, the positive effect of the ketogenic diet on epilepsy is well documented - and has been researched for over 100 years. The keto diet is an official therapeutic measure for the treatment of epilepsy - especially in children and adolescents who frequently suffer from epileptic seizures and cannot be controlled well with medication. In 50 to 75 per cent of cases, the seizures either disappear completely or are significantly reduced by switching to the keto diet.
Influence of the ketogenic diet on the immune system
A study by the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich found that the keto diet led to a significant improvement in the performance of T-cell immunity after just three weeks - T-cells play an important role in recognising antigens and killing the body's own infected cells. This means that the ketogenic diet could play a role in the treatment of numerous diseases in the future. However, research on this topic is still in its infancy. Professor Kreth from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich also suspects that incorporating ketogenic phases into the diet could have positive effects on the prevention of diseases - although this too has yet to be confirmed by clinical studies.
Cancer prevention through a ketogenic diet?
Some sources recommend a ketogenic diet for cancer, as some cancer cells need sugar in particular to divide. Although the keto diet cannot cure cancer, it can slow down its growth. Ketosis would also help with treatment, as the drugs respond better and the body breaks down less. However, according to the German Cancer Society and the German Society for Nutritional Medicine, methodologically high-quality studies are lacking for this information. The current recommendation of these institutes is therefore a balanced mixed diet.
Good to know:
How do you recognise oral cavity cancer and what does the treatment look like? You can find all the information here:
Further health benefits
Many keto followers feel "fitter" and more energised with the ketogenic diet. They also report that they can concentrate better.
As sugary and industrially manufactured products are largely eliminated, a ketogenic diet often has a positive effect on the appearance of the skin and reduces acne. When overweight people lose weight on the keto diet, their blood pressure usually drops too.
Disadvantages of the ketogenic diet
Although the potential benefits of the ketogenic diet are impressive, they have not yet been sufficiently proven. The long-term effects of the ketogenic diet have also not yet been sufficiently investigated. This is why many nutritionists and doctors consider the ketogenic diet to be too one-sided. As entire food groups such as most fruit, pulses, cereals and starchy vegetables are excluded, a nutrient deficiency could arise in the long term. A change in the electrolyte balance can also increase the risk of kidney stones. It is therefore often recommended that the keto diet should only be used for a limited period of time and then switched to a balanced, healthy diet. In addition, such a restrictive diet can limit the quality of life - especially in social situations with people who eat a "normal" diet - or even cause an eating disorder.
Who is the keto diet not suitable for?
The ketogenic diet is safe for healthy adults in the short term - no long-term effects are known to date. The keto diet is not suitable for people with chronic kidney or liver disease. Diabetics absolutely need medical supervision and should inform their diabetes team about the planned change. As a general precaution, you should check with your doctor whether there are any objections if you want to try the keto diet.
Keto during pregnancy
Whether the ketogenic diet is suitable for pregnant women is still unclear. Some studies suggest that a low-carb diet could increase the risk of birth defects. However, a meta-analysis of the so-called "Louwen diet" found that a change in diet six weeks before birth should have a positive effect on pain during labour without harming the child. This form of nutrition was developed by the gynaecologist and head of obstetrics and prenatal medicine at Frankfurt University Hospital and, like the keto diet, largely avoids carbohydrates.
Good to know:
Speaking of pregnancy: did you know that your dental health can suffer during pregnancy? You can find out what to look out for here:
Short-term side effects
During the transition period when your body is changing its metabolism, side effects can occur, which usually subside after a few days. This is also referred to as the "keto flu".
The following symptoms may occur:
- Listlessness/reduced performance
- Tiredness
- Headache
- Lack of concentration
- Nausea to the point of vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhoea
- Increased feeling of hunger
Taking electrolytes can alleviate these symptoms.
Acidic bad breath with ketosis
One of the signs that your body has made the switch to ketosis is a sour acetone odour from the mouth. This "keto mouth odour" occurs when the body is not yet fully "keto-adapted" and is not utilising all the ketones. As soon as the muscles and brain are supplied with ketones, the bad breath should also decrease. The duration of ketosis mouth odour is around one week to one month. Drinking plenty of fluids, brushing your teeth frequently and chewing gum (for example the 'Black is white' chewing gum from Curaprox) will help to keep your breath fresh.
Good to know:
You can find out what else helps against bad breath in our article:
Sources
AWMF online: Guidelines of the Society for Neuropaediatrics: Ketogenic Nutritional Therapies (KET).
Accu Check: Diabetes: Difference between ketosis and ketoacidosis.
Ache, Margret: Experience report type 1 diabetes and keto, on: lchf-deutschland.de
Antwerpes, Frank et al: T-cell and prediabetes, at: flexikon.doccheck.com
Brehm, Bonnie J.: A randomised trial comparing a very low carbohydrate diet and a calorie-restricted low fat diet on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors in healthy women, in: The Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2003.
Brouns, Fred: Overweight and diabetes prevention: is a low-carbohydrate-high-fat diet recommendable?, in: European Journal of Nutrition. 2018.
German Nutrition Society: Eating and drinking well - the DGE recommendations.
German Cancer Research Centre: Sugar and carbohydrates in cancer: Harmful or indispensable?
Dr Gerald Gaß & Partner: How the keto diet can affect your teeth.
Eatbetter: Ketogenic diet - top 15 foods for ketogenic diet.
Fachgesellschaft für Ernährungstherapie und Prävention (FET): Ketogenic diet: Much more than just a trend.
Gardemann, Clemens et al: Managing type 1 diabetes mellitus with a ketogenic diet, in: Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism Case Reports. 2023.
Goldenberg, Joshua Z: Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished randomised trial data, in: BMJ. 2021.
Harvard Health Blog: Ketogenic diet: Is the ultimate low-carb diet good for you?
Harvard School of Public Health: Diet Review: Ketogenic Diet for Weight Loss.
Healthline: 20 Foods to Eat on the Keto Diet and The Ketogenic Diet: A Detailed Beginner's Guide to Keto.
Hirschberger, Simon et al: Very-low-carbohydrate diet enhances human T-cell immunity through immunometabolic reprogramming, in: EMBO Molecular Medicine. 2021.
Kaiser, Berta: Louwen diet: Does it help during labour?, on: netdoktor.de.
Cook Keto: Keto & Low Carb Recipes.
Lennerz, Belinda S. et al: Behavioural Characteristics and Self-Reported Health Status among 2029 Adults Consuming a "Carnivore Diet", in: Current Developments in Nutrition. 2021.
Lipoedema Centre Munich: Ketogenic diet for lipoedema.
LMU Klinikum: Influence of a ketogenic diet on the immune system.
Masood, Wajeed et al: Ketogenic Diet, in: StatPearls. 2023.
McMains, Vanessa: Study: Low-carb Atkins-style diet may modestly improve cognition in older adults, at: hub.jhu.edu.
Meyer, Rüdiger: Diabetes Typ 1: Strict low-carbohydrate diet improves HbA 1c values, on: aerzteblatt.de.
Newman, John C. et al: Ketogenic Diet Reduces Midlife Mortality and Improves Memory in Aging Mice, in: Cell Metabolism. 2017.
Pomer, Laura: Experts explain the benefits of the ketogenic diet, on: fitbook.de.
Roberts, Megan N. et al: A Ketogenic Diet Extends Longevity and Healthspan in Adult Mice, in: Cell Metabolism. 2017.
Röcker, Annika: What are the benefits of a ketogenic diet, on: apotheken-umschau.de
Rusek, Marta: Ketogenic Diet in Alzheimer's Disease, in: International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019.
Schaller, Julian: Advantages and disadvantages of a ketogenic diet, on: swrfernsehen.de.
Ułamek-Kozioł, Marzena et al: Ketogenic Diet and Epilepsy, in: Nutrients. 2019.
Weber, Daniela D. et al: Ketogenic diet in cancer therapy, in: Aging. 2018.
Westman, Eric C. et al: The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus, in: Nutrition & Metabolism. 2008. and Implementing a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus, in: Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2018.
Yancy, William S. et al: A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to treat type 2 diabetes, in: Nutrition & Metabolism. 2005.
Dentists at the Klinik am Ring: bad breath with a keto diet and low carb.
ZWP Online: Keto diet: A high on a sugar-free diet?
All websites last accessed on 15/05/2024.
 Swiss premium oral care
Swiss premium oral care